Table of Contents
ToggleHave you ever bumped into something and thought, “Great, just what I needed—another lump”? If that lump is a hematoma and it’s decided to stick around longer than your last house guest, you might be in for a bit of a conundrum. While most hematomas are just temporary guests that pack their bags and leave, some can linger like an unwelcome party crasher.
Understanding Hematomas
Hematomas are localized collections of blood outside of blood vessels. They typically occur due to an injury or trauma, but some may require further attention if they do not resolve as expected.
What Is a Hematoma?
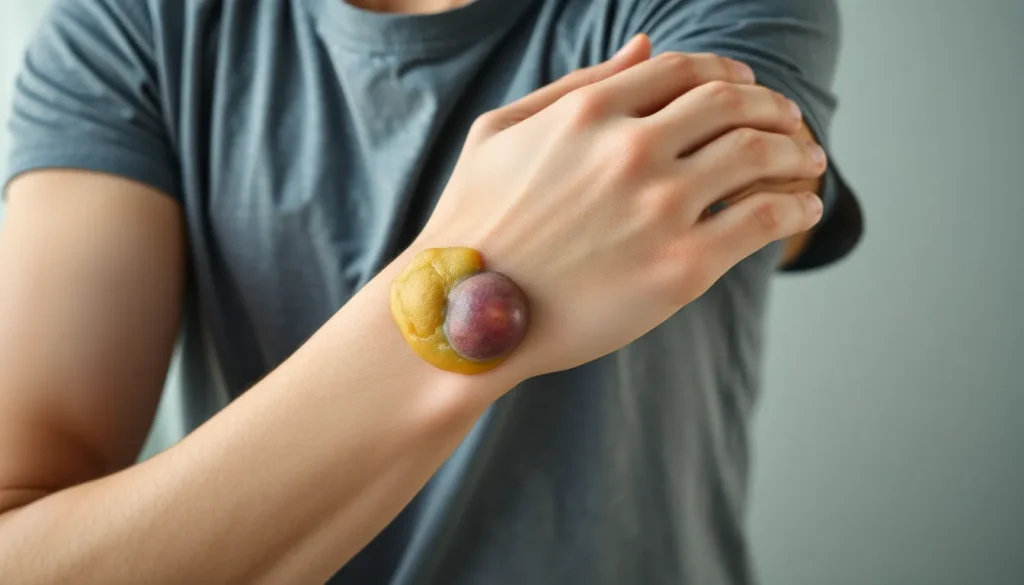
A hematoma forms when blood leaks from damaged blood vessels into surrounding tissue. This causes swelling and discoloration in the affected area. Common symptoms include pain and tenderness. Hematomas can vary in size, from small lumps to larger masses, depending on the severity of the injury. Most hematomas resolve on their own within weeks, while persistent ones may indicate an underlying issue that requires medical assessment.
Common Causes of Hematomas
Injury is the primary cause of hematomas. Falls, sports accidents, or blunt force trauma often lead to this condition. Other causes include surgical procedures and certain medical conditions that affect blood clotting. Aging also plays a role, as skin and blood vessels become more fragile over time. Hematomas can result from repeated movements or overuse, such as in athletes. Recognizing the cause helps in managing the hematoma effectively.
Symptoms of Persistent Hematomas
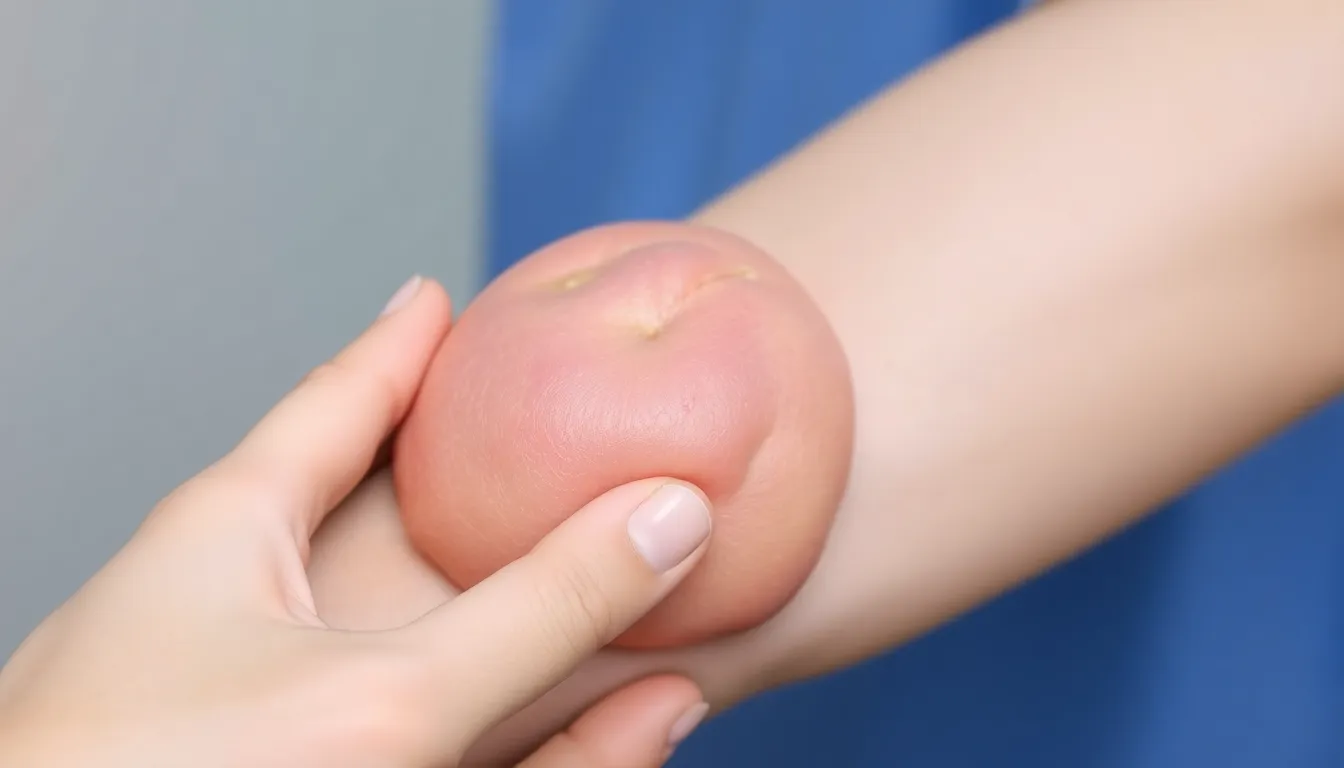
Persistent hematomas may exhibit specific symptoms that signal the need for further evaluation. Common signs include ongoing swelling, changes in color, pain, and tenderness that don’t subside over time.
Identifying a Hematoma Lump
A hematoma lump usually appears as a raised area, often firm to the touch. Discoloration may range from purple to yellowish-green as it heals. Pain level can fluctuate, but persistent discomfort may indicate complications. If the lump feels warmer than surrounding tissue, increased blood flow might signal infection or other issues. Noticing these changes prompts monitoring and potential medical consultation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial if pain worsens or the hematoma grows larger. Signs of infection, such as fever, increased redness, or swelling, warrant immediate attention. Difficulty in mobility or functionality associated with the injury also requires evaluation. Pre-existing medical conditions affecting blood clotting or circulation elevate the risk of complications, making timely medical advice essential. Observations of these symptoms can guide decisions for proper care and interventions.
Potential Complications
Persistent hematomas can lead to various complications if left untreated. The risks associated with untreated hematomas include infection, increased swelling, and even blood clot formation. Infection can occur when blood outside the vessel becomes stagnant, providing a breeding ground for bacteria. Signs of infection often include fever, increased redness, or warmth in the affected area. Increased swelling can compress surrounding tissues, potentially leading to additional pain or discomfort. Blood clots may also develop, posing risks of deep vein thrombosis or other vascular issues.
Long-term effects of persistent hematomas can significantly impact health. Chronic pain may develop, affecting mobility and daily activities. Skin changes, such as discoloration or scarring, can occur as the body heals. Additionally, unresolved hematomas might place pressure on nerves or blood vessels, leading to complications like restricted blood flow or numbness in surrounding areas. Consulting a medical professional remains crucial to address these concerns effectively.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options exist for addressing persistent hematomas. These approaches range from simple home remedies to more advanced medical procedures.
Home Remedies for Hematomas
Cold compresses offer immediate relief by reducing swelling and numbing pain. Elevating the affected area assists in minimizing blood flow to the site, helping to limit further bruising. Over-the-counter pain relievers may reduce discomfort effectively. Gentle massage around the hematoma (not directly on it) can promote circulation, potentially aiding in the healing process. Staying hydrated supports overall health, which may improve recovery times for hematomas.
Medical Treatments and Procedures
A medical professional can provide thorough evaluations for persistent hematomas. If a hematoma shows signs of infection, antibiotics may be necessary to address the condition. Drainage can relieve pressure and expedite healing, especially if the hematoma is large or causing discomfort. In more severe cases, surgical intervention might be required to remove the hematoma. Imaging techniques like ultrasound may assist in evaluating the extent of the hematoma and guiding treatment decisions. Regular medical assessments are essential for anyone experiencing ongoing issues with hematomas.
A persistent hematoma can be more than just a minor inconvenience. It’s essential for individuals to pay attention to their symptoms and seek medical advice when necessary. Ignoring ongoing pain or changes in the lump could lead to complications that might require more intensive treatment.
Taking proactive steps like monitoring the hematoma and utilizing home remedies can aid in recovery. However, when symptoms worsen or do not improve, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. Early intervention can help prevent long-term issues and ensure proper healing. Awareness and timely action can make all the difference in managing a hematoma effectively.







